For a long time, consumers have tolerated the lack of technology found at traditional banks. But with fintech on the rise, banks are struggling to keep up and offer customers the innovation they crave. The question is, will it be fintech vs traditional banks? Or can they join forces to build financial services that modern consumers are looking for?
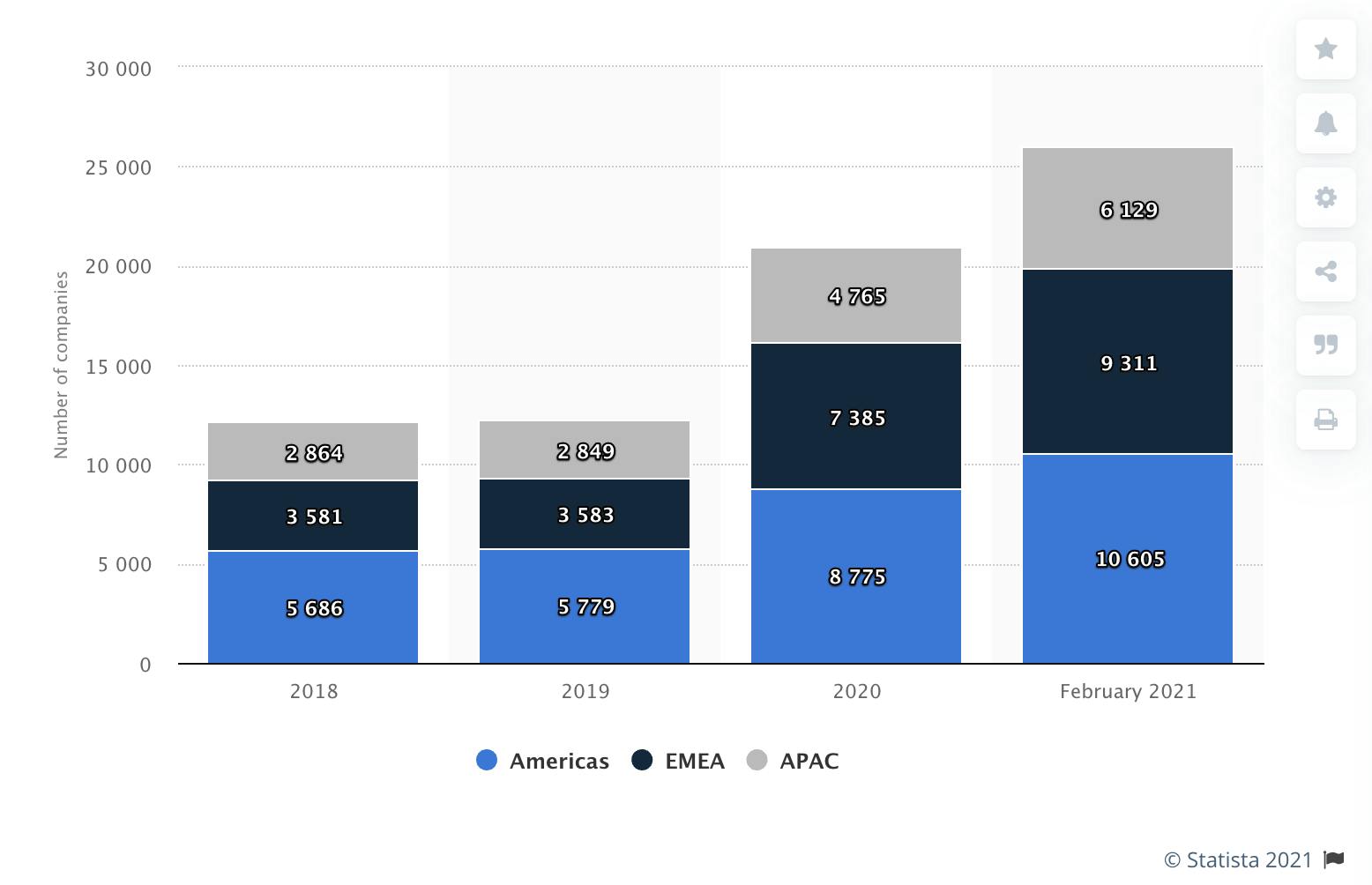
Image source: Statista
According to Statista, from 2018 to 2021, the number of fintech companies in the EMEA region nearly tripled. And in 2018 alone, a total of $254 billion was invested globally into roughly 18,000 fintech startups through venture capital funds.
Fintech is a booming industry that combines financial services and technology to help people and businesses manage payments and financing. But will it last?
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what fintech is, the differences between fintech and traditional banks, and the growth potential of financial technology.
Let’s dive in.
What is Fintech?
Fintech is a combination of the words “financial” and “technology”. It’s a term used to describe new technology that aims to automate and improve the use and delivery of financial services and products.
Fintech is used to help business owners, companies, and consumers easily manage their finances and business processes using software. The technology is usually accessible via their computer or other devices such as a smartphone or tablet.
Fintech began in the late 1990s when the Internet and e-commerce businesses emerged. By the 21st Century, the technology was used at the backend systems of financial institutions to digitize banking.
Since then, fintech has shifted its focus to consumer-oriented services. It’s now used in various industries including retail banking, investments management, fundraising and nonprofit, education, and financial services for individuals. Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are also part of fintech development.
💡 Read also: QR Code Payments: What They Are, How They Work, and How to Accept Them
What are banks?
Traditional banks are financial institutions that are licensed to receive deposits from and make loans to individuals and businesses. Some banks also offer other financial services including wealth management, safe deposit boxes, and currency exchange.
There are various types of banks such as corporate banks, retail banks, and investment banks. And, in most countries, they’re usually regulated by a central bank or the national government.
Why is fintech growing?
According to McKinsey, during the first few months of COVID-19, the use of mobile banking channels increased by 20-50%, and it’s predicted to remain this way even after the pandemic is over.
Another study from McKinsey reports that when it comes to digital banking, consumers are demanding a more flexible journey. 71% prefer multi-channel interactions and 25% want a fully digitally-enabled private banking journey with remote human assistance available when needed. Consumer payment trends are also evolving.
To meet customers’ demand for speed, efficiency, and a better user experience, financial providers need to integrate technology into their services. This will enable them to offer the frictionless experience consumers have come to expect. If retail giants like Amazon let customers complete a purchase in seconds, it shouldn’t require a face-to-face meeting to open a new bank account.
Fintech is bridging the gap between what traditional banks offer and what the modern consumer has grown to expect. The industry has experienced massive growth. In fact, according to The Business Research Company, the global fintech market was valued at about $127.66 billion in 2018 and is expected to grow to $309.98 billion at an annual growth rate of nearly 25% through 2022.

Image source: Toptal
Will fintech last?
Fintech is considered the future of banking and financial institutions, which is why it’s not surprising that the top 50 fintech companies in Europe have raised over $16.8B (€14.3B) in venture capital funding and are valued, collectively, at over $92B (€78B).
Traditional banks have evolved drastically in the way they function thanks to new-age technologies including machine learning, AI, and analytics. Banks have also begun to acquire fintech startups to add to their services. In addition, fintech startup accelerator programs are gaining popularity, some of which are managed by banks including ING and JPMorgan.
The competition is intense, so some fintech businesses will thrive while others could struggle to stay afloat. But this presents an opportunity for fintech startups and traditional banks to team up and adapt quickly to the new digital world.
Fintech vs traditional banks: what’s the difference?
While fintech and traditional banks both aim to provide seamless financial services to consumers, that’s really the only similarity.
Fintech’s are considered the bank’s biggest competitors. The financial system banks use today is made up of some very traditional and antiquated practices and procedures. It’s more often time-consuming and glitchy than it is frictionless. As consumer demands continue to shift to wanting things faster and easier, people are looking for a financial solution that meets their needs.
When it comes to innovation and advancement, traditional banks are falling behind and fintech is stepping up to the plate. Fintech may have a small share in the world banking system, but consumers are increasingly opting to use it as a substitute to banks.
According to Statista, between 2015 and 2019, consumer adoption of fintech companies and products grew rapidly worldwide. By 2019, 75% of consumers globally started using some form of money transfer and/or payment service.
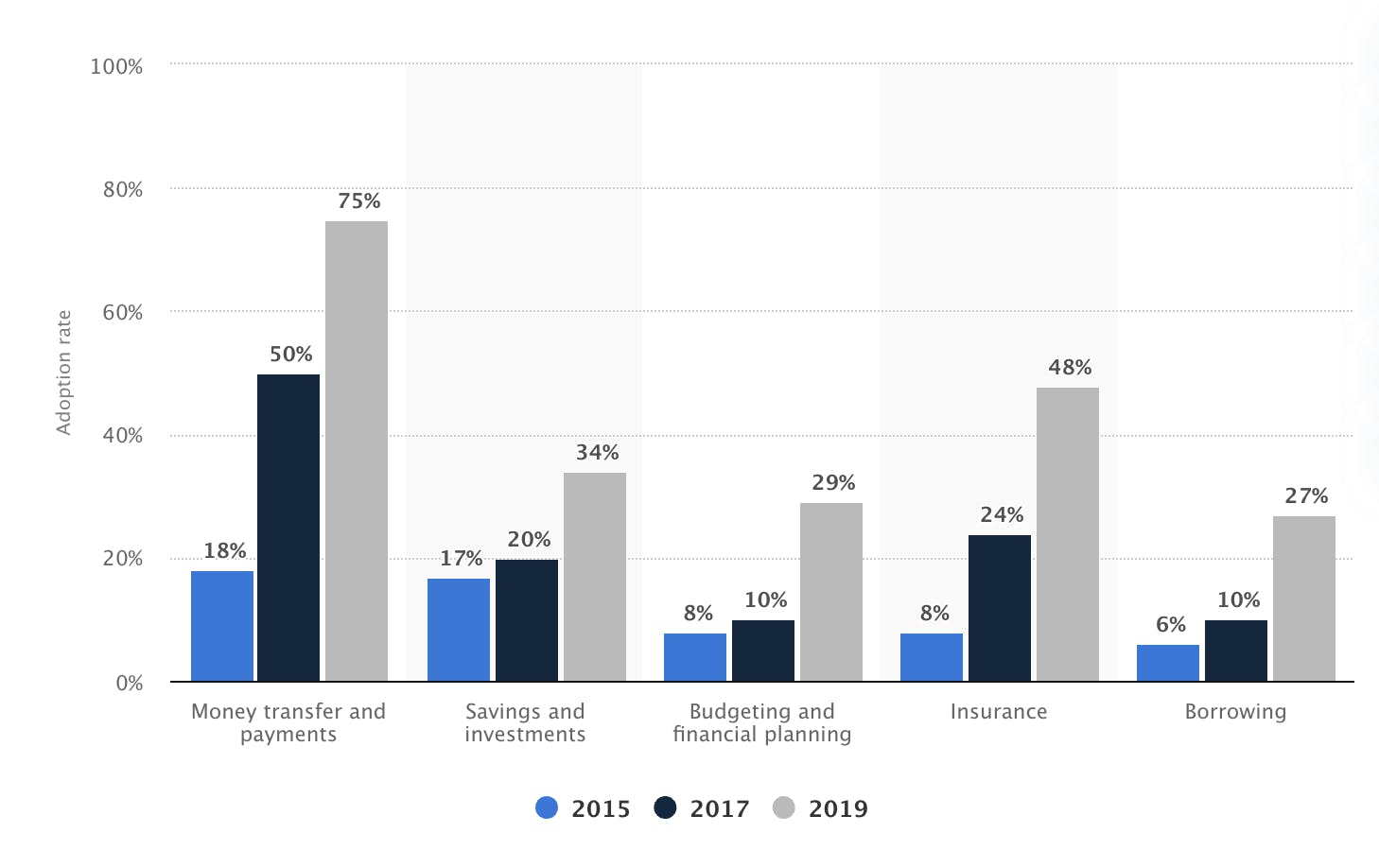
Image source: Statista
We can break down the differences between fintech and traditional banks into four categories.
- The way of doing business
- Regulations
- Growth potential
- Risk factors
1. The way of doing business
Traditional banks and fintech companies both operate as financial service providers, but have different ways of doing business.
Structure and function
Fintech
Fintech is innovative, customer-centric, and streamlines complex financial processes, making it more accessible to people. These types of companies use lean operating models that are free of legacy system issues and can circumvent unfavorable regulations. Because of the flatter organizational structures in fintech, it’s easier to change, innovate, and rebuild systems that aren’t working.
Fintech leverages new technologies like artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing to give customers a unique experience. It’s focused on seamless delivery, personalization, speed, and relevance.
By streamlining complex financial processes, fintech’s are more accessible to people, particularly millennials and younger generations.
Also, due to a more optimized business structure, fintech companies can offer products and services that are up to 10 times less expensive than traditional banks. A traditional bank needs real estate and thousands of employees while many fintech’s need very little real estate and a smaller team. The savings are then passed on to consumers.
Traditional banks
The legacy systems and regulatory framework that banks use restrict their ability to leverage new technologies in time. For this reason, banks can’t introduce new services or products that address customer needs or issues at the same speed as fintech companies. Overall, banks are more process-oriented when compared to fintech.
Customer experience
Fintech
Fintech’s are agile and accessible. They work virtually, so consumers don’t need to physically be present to transact or partake in financial services. This makes fintech a convenient option. Users can register on their computer, or in most cases, via an app on their mobile device. Fintech’s offer 24/7 access, remote account opening, quick consultations, and better communication with customers overall. They have grown due to their focus on user experience, which is where banks have fallen behind.
💡Further reading: 8 Trends Shaping the Future of Payments & E-commerce
Traditional banks
In most cases, banks require you to be physically present to open an account or to apply for financial services. Not all banks have the technology to verify your identity online. This makes traditional banking less convenient for consumers, leading to an unsatisfactory experience.
Technology
Fintech
Fintech’s build on technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and automation to function faster. Using technology also leads to fewer mistakes, higher quality service, and faster service in a shorter amount of time.
Traditional banks
When it comes to technology, banks are still struggling with legacy infrastructure. These banking systems are usually decades old, and support the bank’s operations and backend across its main functions. This includes opening an account, setting up an account, processing transactions, deposits, loans, and more. Legacy systems limit the ability to interface with other systems and restrict banks from improving their infrastructure to quickly deliver new services, products, or experiences to customers. For this reason, banks are lagging behind.
2. Regulations
Every financial institution is regulated in some way or another to make it safe for people to use. But fintech is generally more lenient and flexible and banks are stricter.
Fintech
Fintech companies don’t have one particular regulator. This is one reason why so many fintech startups have appeared. Without strict regulation, these companies can make changes to their business and do what they want without strict guidelines. While this makes it easier for fintech startups to work faster and adapt to their users’ needs, some consider it a risky industry. Depending on the country, authorities do regulate fintech businesses. And some companies choose to be more regulated or compliant, so their customers feel safer.
Traditional banks
Banks are regulated by national or central banks in their country of origin. The regulating bodies require banks to adhere to legal requirements, restrictions, and guidelines that are put in place to safeguard their people’s money. Banking regulations are used to ensure transparency between financial institutions and their customers.
3. Growth potential
When comparing two industries, growth is a key factor. Both traditional banks and fintech companies have growth potential depending on different aspects.
Fintech
The pandemic may be a big reason for the digital transformation we saw in 2020, but this trend is here to stay. Fintech Magazine projects that 2021 will be about convenience, inclusion, and sustainability. And this will fuel the growth of financial technologies this year and into the future.
Traditional banks
This doesn’t mean banks will slip away. Traditional banks have sustained market share, and with fintech on the rise, they are acclimating to changes in consumer needs. This includes adopting fintech features like digital security, mobile payments, and peer-to-peer lending, which lets customers borrow from an individual or group of individuals.
4. Risk factors
While fintech may be riskier, its benefits outweigh the risks.
Fintech
Due to the flexible nature of fintech regulations, the industry is considered riskier. But people still use it because it offers a faster, less expensive, more innovative, and highly user-friendly experience. As well as added features that can’t be found at traditional banks.
Traditional banks
Stricter regulations, of course, lead to lower risk, which makes traditional banks the less risky option. But if you want to stay competitive, reach more people, and provide a better customer experience using financial technology is essential. Just make sure you’re using an app or service that is well known and if necessary, is compliant. For example, our payment gateway must be PCI DSS compliant to ensure both merchant and consumer data is securely handled in processing credit card transactions.
Compliance regulations vary depending on the sector each fintech is operating in.
Will fintech companies and traditional banks work together?
Fintech companies and traditional banks both work as financial intermediaries. Banks have been in business for hundreds of years, but they still need to make radical changes to meet the needs of modern-day customers.
Technologically speaking, fintech’s give users more advanced features, and almost all the same services traditional banks provide. So, what does their relationship look like now? And how will it evolve in the future?
We can’t expect people to switch completely away from banks to fintech. But if fintech and banks can cooperate and collaborate, they’ll both make a bigger impact. There are immediate advantages to both parties if the two can partner.
Traditional banks benefit from the innovation and agility of fintech. And they boost confidence in financial technology due to decades of customer loyalty, business size, and an established network.
Here are a few advantages to fintech and traditional banks collaborating:
- When compared to fintech, banks have huge deposits. If they partner, building better financial systems will be easier for banks.
- If fintech collaborates with banks, they will be regulated under the same government institutes which can help build trust.
- The overall financial system will improve because of the advanced technology fintech can bring to banking.
To meet the technological demands that consumers have today, banks are embracing fintech features to improve user experience. As the whole finance system continues to evolve, allocating resources for digital agility is increasingly a priority for banks. A win-win situation for both is long-term partnerships that combine innovation (fintech) and support and trust (banks) to build the sector for the digital future.